Difference between revisions of "Lake San Salvador"
m (Text replacement - "Creeperian Spanish" to "Creeperian") |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{short description|Natural lake in Creeperopolis}} | ||
| + | {{use dmy dates|date=November 2021}} | ||
{{Infobox body of water | {{Infobox body of water | ||
| name = Lake San Salvador | | name = Lake San Salvador | ||
| − | | native_name = Lago San Salvador | + | | native_name = Լագո Սան Սալվադոր<br />Lago San Salvador |
| − | |||
| − | |||
<!-- Images --> | <!-- Images --> | ||
| − | | image = Lake Erie Land's End.jpg | + | | image = [[File:Lake Erie Land's End.jpg|300px|The shore of Lake San Salvador as seen from La'Unión.]] |
| − | | | + | | caption = The shore of Lake San Salvador as seen from [[La'Unión (department)|La'Unión]]. |
| − | | caption | + | | image_map = |
| − | | | + | | caption_map = |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
<!-- Stats --> | <!-- Stats --> | ||
| − | | location = [[ | + | | location = Central [[Sur]] |
| − | | group = [[ | + | | group = [[Great Creeperian Lakes]] |
| − | | coordinates = | + | | coordinates = [[File:WMA button2b.png|17px|link=Creeperopolis]] {{color|#3366BB|45°34′46″S 57°17′11″W}} |
| − | | type = | + | | type = Tectonic lake |
| − | | etymology = | + | | etymology = "Lake of the Holy Savior" in [[Creeperian language|Creeperian]] |
| − | | | ||
| inflow = [[San Miguel River]] | | inflow = [[San Miguel River]] | ||
| − | |||
| outflow = [[Asambio River]] | | outflow = [[Asambio River]] | ||
| − | | | + | | basin_countries = {{flag|Creeperopolis}} |
| − | + | | designation = [[Creeperopolis National Historical Landmarks|Creeperopolis National Historical Landmark]] (since 15 September 1960) | |
| − | + | | area = 23,858 sq mi (61,791 km<sup>2</sup>) | |
| − | + | | max-depth = 1,148 ft (350 m) | |
| − | | designation = | + | | volume = |
| − | + | | residence_time = 284 years | |
| − | + | | shore = 935 mi (1504 km) | |
| − | + | | islands = 18 ([[Lake San Salvador#Islands|see list]]) | |
| − | + | | cities = [[Bautista, San Salvador|Bautista]], [[Escuinbulco, San Salvador|Escuinbulco]], [[La'Mirada, San Salvador|La'Mirada]], [[La'Unión, La'Unión|La'Unión]], [[La'Victoria]], [[Nuevo San Salvador, San Salvador|Nuevo San Salvador]], [[San Salvador, San Salvador|San Salvador]], [[San Salvador del Norte, San Salvador del Norte|San Salvador del Norte]], [[South Serrada, San Salvador|South Serrada]], [[Terrarote, San Salvador|Terrarote]] | |
| − | |||
| − | | area = | ||
| − | |||
| − | | max-depth = | ||
| − | | volume = | ||
| − | | residence_time = | ||
| − | |||
| − | | shore = | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | islands = | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Lake San Salvador''' ([[Creeperian | + | '''Lake San Salvador''' ([[Creeperian language|Creeperian]] – [[Creeperian script|Creeperian]]: Լագո Սան Սալվադոր; Creeperian – [[Iberic script|Iberic]]: ''Lago San Salvador'') is a tectonic lake in central [[Creeperopolis]]. It is the second largest lake in the world by surface area and the largest in [[Sur]] and the Southern Hemisphere. The lake's primary inflow is the [[San Miguel River]] in the north and its primary outflow is the [[Asambio River]] in the south. |
| − | [[File:Lake San Salvador.png|thumb| | + | The lake is the seventh deepest in Creeperopolis with a maximum depth of 1,148 ft (350 m), and has a shoreline of approximately 935 mi (1504 km). It is categorized as a member of the [[Great Creeperian Lakes]] group, along with [[Lake Atlántida]], [[Lake Castilliano]], and [[Lake Zapatista]]. |
| + | |||
| + | == Etymology == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lake San Salvador is named after the city of [[San Salvador, San Salvador|San Salvador]], which itself is named after [[Yeshua|Jesus Christ]], the central figure of [[Christianity]] and the [[Creeperian Catholic Church]]. Lake San Salvador means "Lake of the Holy Savior" in [[Creeperian language|Creeperian]], where it is rendered as Լագո Սան Սալվադոր ([[Creeperian script]]) or ''Lago San Salvador'' ([[Iberic script]]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [[Hondurans]] referred to the lake as "The Great Lake" ([[Honduran language|Honduran]]: ''Aintzira Handia''). The lake was known as the "Lake of the Messenger" ([[Deltinian language|Deltinian]]: بحيرة الرسول; transliterated as ''Buhayrat al-Rasul'' or ''Buhayrat Alrasul''). The name was in reference to [[Muhammad]], the central figure and most important prophet of [[Islam]], and was used from the 10th century to the 14th century. The lake was also known as the "Lake of the Victory" (''Lago de la'Victoria'') from the 14th century until the mid-16th century, as it was called by the Kingdom of Creeperopolis. During the mid-16th century, the lake it became known as Lake San Salvador. | ||
| + | |||
| + | During the [[Creeperian Civil War]], as a part of its [[Secularization (Creeperopolis)|Secularization]] process, the [[National Council for Peace and Order]] temporarily renamed the lake to "Great Central Lake" (''Gran Lago Central'') in 1933. In 1934, the National Council renamed the lake to "Lake Ordóñez Yepes" (''Lago Ordóñez Yepes''), commemorating [[National Liberal Party (Creeperopolis)|National Liberal]] politician [[Inhué Ordóñez Yepes]]. The name change was not recognized by the opposing [[Catholic Imperial Restoration Council]] which retained the name Lake San Salvador; the name Lake Ordóñez Yepes was abandoned following the end of the civil war in 1949. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Geography == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Location and size === | ||
| + | |||
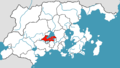
| + | [[File:Lake San Salvador.png|thumb|right|250px|The location of Lake San Salvador in red.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lake San Salvador is located in central [[Creeperopolis]] and is surrounded by the [[Departments of Creeperopolis|departments]] of [[La'Unión (department)|La'Unión]], [[San Luís (department)|San Luís]], [[San Salvador (department)|San Salvador]], [[San Salvador del Norte (department)|San Salvador del Norte]], and [[Santa Ana (department)|Santa Ana]]. The lake's primary inflow is the [[San Miguel River]] in the north and its primary outflow is the [[Asambio River]] in the south which drains into [[Lake Zapatista]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The lake has a surface area of 23,858 sq mi (61,791 km<sup>2</sup>), making it the second largest lake in the world after [[Lake Manal]] in central [[Ecros]]. Lake San Salvador is the largest lake in [[Sur]] and the largest in the southern hemisphere. The lake's maximum depth is 1,148 ft (350 m), making it the seventh deepest lake in Creeperopolis. Its shoreline is approximately 935 mi (1504 km) long. The lake's water has a residency time of 284 years. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Islands === | ||
| + | |||
| + | The lake has eighteen islands, with the largest being [[Isla San Romero (Lake San Salvador)|Isla San Romero]], which itself has two lakes on it. Seventeen of the eighteen of the islands are visible from the shoreline. The lone exception is [[Isla Lejos (Lake San Salvador)|Isla Lejos]] which is located 24 mi (39 km) southeast of [[San Salvador del Norte, San Salvador del Norte|San Salvador del Norte]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | All of the islands of Lake San Salvador in order of largest to smallest are: | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{div col|colwidth=15em}} | ||
| + | * [[Isla San Romero (Lake San Salvador)|Isla San Romero]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla de la'Gran Victoria]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla Puyal Cisneros]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla Bendita]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla San Salvador Mayor]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla Santa Ana]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla Punto Norte]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla del Santo Bautista]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla Miguel I]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla de Jesús (Lake San Salvador)|Isla de Jesús]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla Suchitlán]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla Pequín]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla de Morelos]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla Santa Cruz (Lake San Salvador)|Isla Santa Cruz]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla Espiga Mina]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla de La'Unión]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla San Salvador Menor]] | ||
| + | * [[Isla Lejos (Lake San Salvador)|Isla Lejos]] | ||
| + | {{div col end}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Cities === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Various major important cities are located on the shore of Lake San Salvador. In addition to the country's capital city of San Salvador, the cities of [[Bautista, San Salvador|Bautista]], [[Escuinbulco, San Salvador|Escuinbulco]], [[La'Mirada, San Salvador|La'Mirada]], [[La'Unión, La'Unión|La'Unión]], [[La'Victoria]], [[Nuevo San Salvador, San Salvador|Nuevo San Salvador]], San Salvador del Norte, [[South Serrada, San Salvador|South Serrada]], and [[Terrarote, San Salvador|Terrarote]] are also located on Lake San Salvador. Each of the cities on the lake have sea ports and fisheries which serve important roles in the individual cities' economies. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Lake environment == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Climate === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Ecology === | ||
| + | |||
| + | The lake is populated by various fish species, and although it is a freshwater lake, sharks and dolphins which migrated from the [[Southern Ocean]] have been found in the lake. Many plant species grow around the lake and various bird species use the lake to hunt for fish. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == History == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === First human settlement === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Deltinian period === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Creeperian control and modern history === | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Economy == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Fishing === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Tourism === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Shipping traffic === | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Shipwrecks == | ||
| + | |||
| + | == See also == | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[List of lakes in Creeperopolis]] | ||
{{Oceans, Seas, and Lakes}} | {{Oceans, Seas, and Lakes}} | ||
| Line 71: | Line 120: | ||
[[Category:Creeperopolis Terraconserva]] | [[Category:Creeperopolis Terraconserva]] | ||
[[Category:Terraconserva]] | [[Category:Terraconserva]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Creeperopolis National Historical Landmarks]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:04, 12 March 2024
| Lake San Salvador | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | Central Sur |
| Group | Great Creeperian Lakes |
| Coordinates | |
| Type | Tectonic lake |
| Native name | Լագո Սան Սալվադոր Lago San Salvador |
| Etymology | "Lake of the Holy Savior" in Creeperian |
| Primary inflows | San Miguel River |
| Primary outflows | Asambio River |
| Basin countries | |
| Designation | Creeperopolis National Historical Landmark (since 15 September 1960) |
| Surface area | 23,858 sq mi (61,791 km2) |
| Max. depth | 1,148 ft (350 m) |
| Residence time | 284 years |
| Shore length1 | 935 mi (1504 km) |
| Islands | 18 (see list) |
| Settlements | Bautista, Escuinbulco, La'Mirada, La'Unión, La'Victoria, Nuevo San Salvador, San Salvador, San Salvador del Norte, South Serrada, Terrarote |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
Lake San Salvador (Creeperian – Creeperian: Լագո Սան Սալվադոր; Creeperian – Iberic: Lago San Salvador) is a tectonic lake in central Creeperopolis. It is the second largest lake in the world by surface area and the largest in Sur and the Southern Hemisphere. The lake's primary inflow is the San Miguel River in the north and its primary outflow is the Asambio River in the south.
The lake is the seventh deepest in Creeperopolis with a maximum depth of 1,148 ft (350 m), and has a shoreline of approximately 935 mi (1504 km). It is categorized as a member of the Great Creeperian Lakes group, along with Lake Atlántida, Lake Castilliano, and Lake Zapatista.
Contents
Etymology
Lake San Salvador is named after the city of San Salvador, which itself is named after Jesus Christ, the central figure of Christianity and the Creeperian Catholic Church. Lake San Salvador means "Lake of the Holy Savior" in Creeperian, where it is rendered as Լագո Սան Սալվադոր (Creeperian script) or Lago San Salvador (Iberic script).
The Hondurans referred to the lake as "The Great Lake" (Honduran: Aintzira Handia). The lake was known as the "Lake of the Messenger" (Deltinian: بحيرة الرسول; transliterated as Buhayrat al-Rasul or Buhayrat Alrasul). The name was in reference to Muhammad, the central figure and most important prophet of Islam, and was used from the 10th century to the 14th century. The lake was also known as the "Lake of the Victory" (Lago de la'Victoria) from the 14th century until the mid-16th century, as it was called by the Kingdom of Creeperopolis. During the mid-16th century, the lake it became known as Lake San Salvador.
During the Creeperian Civil War, as a part of its Secularization process, the National Council for Peace and Order temporarily renamed the lake to "Great Central Lake" (Gran Lago Central) in 1933. In 1934, the National Council renamed the lake to "Lake Ordóñez Yepes" (Lago Ordóñez Yepes), commemorating National Liberal politician Inhué Ordóñez Yepes. The name change was not recognized by the opposing Catholic Imperial Restoration Council which retained the name Lake San Salvador; the name Lake Ordóñez Yepes was abandoned following the end of the civil war in 1949.
Geography
Location and size
Lake San Salvador is located in central Creeperopolis and is surrounded by the departments of La'Unión, San Luís, San Salvador, San Salvador del Norte, and Santa Ana. The lake's primary inflow is the San Miguel River in the north and its primary outflow is the Asambio River in the south which drains into Lake Zapatista.
The lake has a surface area of 23,858 sq mi (61,791 km2), making it the second largest lake in the world after Lake Manal in central Ecros. Lake San Salvador is the largest lake in Sur and the largest in the southern hemisphere. The lake's maximum depth is 1,148 ft (350 m), making it the seventh deepest lake in Creeperopolis. Its shoreline is approximately 935 mi (1504 km) long. The lake's water has a residency time of 284 years.
Islands
The lake has eighteen islands, with the largest being Isla San Romero, which itself has two lakes on it. Seventeen of the eighteen of the islands are visible from the shoreline. The lone exception is Isla Lejos which is located 24 mi (39 km) southeast of San Salvador del Norte.
All of the islands of Lake San Salvador in order of largest to smallest are:
- Isla San Romero
- Isla de la'Gran Victoria
- Isla Puyal Cisneros
- Isla Bendita
- Isla San Salvador Mayor
- Isla Santa Ana
- Isla Punto Norte
- Isla del Santo Bautista
- Isla Miguel I
- Isla de Jesús
- Isla Suchitlán
- Isla Pequín
- Isla de Morelos
- Isla Santa Cruz
- Isla Espiga Mina
- Isla de La'Unión
- Isla San Salvador Menor
- Isla Lejos
Cities
Various major important cities are located on the shore of Lake San Salvador. In addition to the country's capital city of San Salvador, the cities of Bautista, Escuinbulco, La'Mirada, La'Unión, La'Victoria, Nuevo San Salvador, San Salvador del Norte, South Serrada, and Terrarote are also located on Lake San Salvador. Each of the cities on the lake have sea ports and fisheries which serve important roles in the individual cities' economies.
Lake environment
Climate
Ecology
The lake is populated by various fish species, and although it is a freshwater lake, sharks and dolphins which migrated from the Southern Ocean have been found in the lake. Many plant species grow around the lake and various bird species use the lake to hunt for fish.