Montesayette
Montesayettean Commonwealth Commonwealth Montesayettien (Quebecshirite) | |
|---|---|
 Location of Montesayette | |
| Capital and largest city | Nerfoy |
| Administrative center | Présidie |
| Official languages | |
| Recognised regional languages | |
| Ethnic groups (2022) |
|
| Religion (2022) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Montesayettean |
| Government | Federal presidential republic |
| Hervé Dufriche-Desgenettes | |
| Marielle Bettencourt | |
| Jean-Baptiste Brisbois | |
| Corbin Perreault | |
| Olivie Fabron | |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Senate | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Formation | |
• Founded | 22 August 1291 |
| 17 April 1825 | |
| 18 December 1828 | |
| 9 June 1920 | |
| 13 May 1921 | |
| 23 September 1993 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,743,230 km2 (673,060 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2023 estimate | |
• 2022 census | |
• Density | 39.53/km2 (102.4/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2023) | low |
| HDI (2023) | high |
| Currency | Montesayettean pound (LSY) |
| Time zone | TMB-2 (HNM) |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy (CE) |
| Mains electricity | 230 V–50 Hz |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +37 |
| ISO 3166 code | SY |
| Internet TLD | .sy |
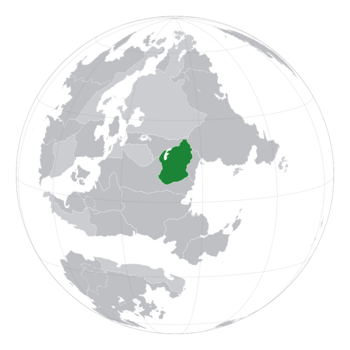
Montesayette, informally Audrecelles and officially the Montesayettean Commonwealth, is a landlocked country in Eastern Ecros. It shares borders with Quebecshire to the northeast, Majocco to the north, Terranihil to the west and south, and Eleutherios to the east. Montesayette is geographically divided among the Audrecelles Plateau, the Aiguilles, and the Montmarin steppe; the Montmarin steppe to the south covers most of the territory, but nearly half of the population is concentrated on the southern shore of Lac de Sandrine on the plateau to the north, home to the nation's largest cities, including Nerfoy, the federal capital. The Aiguilles form a natural barrier between the plateau and the steppe.
The lands of Montesayette have been inhabited since the Paleolithic period. By 400 BCE, the region was home to the Rouchians before being annexed by the Romanyans in the late 1st century BCE. Christianization began in the 4th and 5th centuries, followed by the arrival of various Rhazan tribes during the Migration Period. Montesayette emerged as a unified state from the Montesayettean Confederation in the Late Middle Ages after a series of military victories against Quebecshire and Majocco. For three centuries, petty kingdoms ruled the region until the Lingonian monarchy unified it in 1603. The 16th-century Montesayettean Renaissance saw cultural flourishing but was marred by religious wars between Catholics and Audersellans. Audrecelles, heartland of the Lingonian monarchy, was successful in these conflicts and further increased its influence during the reign of Carina I.
The Audrecellan Revolution of 1788 reduced the role of the Lingonian monarchy and replaced absolutism with a uniquely liberal political system, adopting one of the world’s first modern constitutions. Montesayette reached its political and military zenith in the early 19th century under Jean-Baptiste-Alphonse de Loupershouse, expanding south and annexing the Emirate of Amedi, thereby securing its current borders. However, the annexation led to a rapid decline, marked by sectional conflicts over slavery, serfdom, religion, and the agricultural and industrial revolutions. These tensions led to the secession of the United Republics of Darbonnay and the 1824–1828 First Montesayettean Civil War. During the war, pressure from reformers, the middle class, the upper class, and workers forced the Lingonian monarchy to step down. A provisional government took power, winning the war and preserving the union, while abolishing slavery and serfdom nationwide. The war’s end led to the founding of the Montesayettean Congressional Republic, a federation of labor unions and socialist political parties. In the following decades, Montesayette experienced relative stability and cultural and scientific advancement, amid trials and experiments with syndicalist and socialist policies.
By the 1890s, Montesayette entered a period of stagnation, losing economic importance as protectionist policies hindered growth. This stagnation fueled political violence between socialists and syndicalists, as well as between unionists and regionalists who sought to revive the Montesayettean Confederation. These tensions escalated into the 1918–1919 Second Montesayettean Civil War. Though the socialists won, the war exacted a heavy human and economic toll. Its aftermath saw the Patriation of Montesayette, granting provincial governments autonomy with responsible governance, basic laws, and territorial sovereignty. In 1921, the Montesayettean Commonwealth was proclaimed, replacing the former republic. During the South Ecros War, Montesayette was part of the coalition that attempted to stabilize the Eleutherian and Pavulturilori governments, seeking to prevent communist movements from spreading across its borders. After the war, Montesayette enjoyed a strong recovery, briefly interrupted in the 1960s. Efforts toward further democratization in the late 1980s led to a resurgence of regionalist and secessionist movements, culminating in the Darbonnay Wars between 1991 and 2008. The current Fifth Commonwealth was formed in 1993 by Sévérine Dufour.
Montesayette is a federal presidential republic under its 1991 constitution, with three separate branches: legislative, executive, and judicial. The bicameral federal legislature consists of the House of Representatives, the lower house based on population, and the Senate, the upper house, which provides equal representation for each province and includes corporatist representation. The legal system is mixed; private law follows civil law, while public law, including criminal prosecution, is based on common law. Though the country is de jure a multi-party democracy with free elections, the Social Democratic Party (SD) holds widespread control, maintaining political dominance. The SD has governed continuously and held a supermajority in the House of Representatives since 1973. Substantial autonomy of Montesayette's nine provinces and one autonomous city is provided by federalism.
A developed country with one of the world's largest economies, Montesayette is a global leader in science and technology and the aerospace, robotics, and electronics industries. It is culturally diverse and has one of the highest foreign-born populations in the world. The country's abundant natural resources and strong international trade relations are vital to its economy. Recognized as a middle power, Montesayette's strong support for multilateralism and internationalism has been closely related to its foreign relations policies of peacekeeping and aid for developing countries. Montesayette is a member of several multilateral organizations, including the Terraconserva Council of Nations, the Alliance of Central Ecrosian States, and the Eastern Ecros Free Trade Area.
Contents
Etymology
Montesayette
Montesayette derives from the Quebecshirite name for the Mont Sayette massif. Monte comes from the Quebecshirite word for "mountain," while Sayette traces its roots to sagathy, a fine twilled worsted fabric historically used for clothes and curtains, similar to serge, as the region has been known for its textile industry since antiquity. Initially, "Montesayette" referred only to the petty kingdoms surrounding Mont Sayette. However, during the Montesayettean Confederation, when the seat of power was in the Kingdom of Audrecelles, the term came to include the whole region. This association grew stronger in the early modern period under the Lingonian monarchy which promoted Audrecellan culture as the definitive Montesayettean culture. By the 18th and 19th centuries, the entire region was commonly known as Montesayette.
Audrecelles
The term Audrecelles, or Auderselles in its Old Quebecshirite form, derives from Auder, meaning "river" in Old Quebecshirite, and selles, from the Romanyan Iberic cellas, meaning huts or small dwellings. The name has often been used informally to refer to all of Montesayette in various languages, including Quebecshirite and Jackian. In some cases, it also serves as the formal name for the country. However, Audrecelles is a province of Montesayette, once the Kingdom of Audrecelles before the abolition of the Lingonian monarchy. Due to its prominence during the formation of the Montesayettean Confederation, the religious wars, and the unification under Audrecelles-born Lingonian monarchs, the name Audrecelles became a pars pro toto for the entire nation.
Many Montesayetteans oppose the use of Audrecelles to refer to the country, as it symbolizes not only the former monarchy but also the historical subjugation of other regions by Audrecelles. As of 2023, the Montesayettean government officially prefers Montesayette over Audrecelles when referring to the nation. Additionally, Audrecellan or Audrecellois is often used pejoratively by Darbonnayans to describe Northern Montesayetteans living north of the Aiguilles.
History
Prehistory
Antiquity
Middle Ages
Early modern period
Audrecellan Revolution
Southward expansion and First Civil War
Long nineteenth century
Second Civil War and patriation
Dieulafoyan period and South Ecros War
Post-war and contemporary eras
Geography
Climate
Biodiversity
Government and politics

Montesayette has been a symmetric federation of nine provinces and the autonomous city of Nerfoy since 2014, and a presidential republic since 1973. Before the establishment of the Fifth Commonwealth, the country faced political turmoil and democratic reversals. From 1962 to 1972, Montesayette endured an unstable parliamentary system, characterized by political violence and weak minority governments. In 1972, a military coup overthrew the government, creating a hybrid regime that lasted nearly 20 years. A democratic transition began in 1986, culminating in the approval of the Constitution of the Fifth Commonwealth by a constituent assembly on 15 July 1991, which took effect on 23 September 1993. The Constitution has been revised once since. Except for the short-lived Third Commonwealth, Montesayette has consistently maintained a presidential system with an independent executive.
Montesayette is classified by academics as an illiberal democracy or soft authoritarian state due to the dominance of the Social Democratic Party (SD), a big-tent party of power that faces little meaningful political competition. Montesayette's multi-party system is considered "minimal," with greater emphasis placed on economic development and social order. Scholars attribute the country's reluctance to fully democratize to its history of political violence and instability, which were more common during periods of greater political participation. As of 2023, Montesayette ranks 16th in the Global Democracy Index and is labeled a "flawed democracy."
National government
The federal government of Montesayette, headquartered in Nerfoy, is composed of three branches. Unlike in most presidential systems, the separation of powers in Montesayette is only partial. The first three chapters of the Constitution are titled "The National Assembly," "The Executive Government," and "The Judicature," with each beginning by vesting the relevant "power of the Commonwealth" in specific persons or bodies. However, Montesayette also follows the principle of responsible government, where the legislature and executive are implicitly connected. In addition to the traditional functions of law-making, adjudication, and execution, Montesayettean constitutional law defines three further state powers: machinery of government, oversight and integrity assurance, and mediation.
- The National Assembly, a bicameral legislature composed of the Senate and the House of Representatives, enacts federal law, declares war, approves treaties, controls public spending, holds impeachment powers, and exercises legislative vetoes. The House of Representatives has 150 members, known as membres du parlement, each representing single-member constituencies of roughly equal population, commonly called "electorates" or "seats." They are directly elected by plurality-runoff for five-year terms, with a limit of three terms. The House holds the exclusive right to introduce money bills and constitutional amendments. The Senate consists of 50 members serving semi-fixed six-year terms with no term limits. Ten senators are appointed by the president, ten are elected from each of Montesayette’s provinces by plurality-runoff, and thirty are chosen through indirect limited voting. In this process, qualified citizens, registered as candidates within vocational panels, vote for one another, with seats awarded by plurality. The Senate reviews legislation, oversees the government, and examines public policy. While it cannot block bills outright, except in rare cases, it can delay their passage for up to a year. If the Senate rejects a bill twice, it triggers a double dissolution, leading to snap elections for both chambers.
- The executive branch is led by the President of the Montesayettean Commonwealth, who is directly elected by universal adult suffrage for a seven-year term with no term limits. The president serves as head of state, chief executive of the federal government, during wartime, and head of the Montesayettean Defense Forces. The president holds absolute veto power over legislation, except in constitutional matters, but cannot issue partial vetoes. They may also use an amendatory veto or refer bills to the Constitutional Court for review. The president can dissolve the House of Representatives but not the Senate, and may bypass the legislature by submitting referendums directly to the public. Presidential appointments to the State Council, including the Prime Minister, require National Assembly approval, and the president names officials who administer and enforce federal laws through their agencies. The president also appoints judges, negotiates international agreements, and has the power to pardon or grant clemency for federal crimes. Additionally, the president has "reserve powers" to declare a legislative emergency, allowing the federal government to enact policies without National Assembly approval, though these actions are subject to later scrutiny.
The Civil Service is constitutionally recognized as its own branch of state power, though it operates under the leadership of the executive branch's political leaders. Each federal department is headed by a permanent secretary, the highest-ranking non-political civil servant, who holds the position for several years. Permanent secretaries advise and report to the ministers overseeing their respective departments. Similarly, statutory boards, which may or may not report to a ministry, are led by chairs appointed and dismissed at the discretion of the federal government. These chairs receive reports and advice from chief executives, who function in the same capacity as permanent secretaries. In addition to the Civil Service, the Advocate-General, the National Ombudsperson, the Electoral Commission, and the Monetary Authority of Montesayette—each non-partisan and appointed by the National Assembly—are all considered independent branches of state power under the Constitution’s oversight and integrity assurance provisions.
Law
Administrative divisions
Montesayette is a symmetric federation of nine provinces—Audrecelles (AUD), Pays de la Sandrine (PDS), Sud-Val de Sandrine (SVS), Grand Ouest (GO), Nouvelle-Darbonnay (NVD), Hamicourt (HAM), Île-de-Fleurs (IF), Hauteurs de Sayette (HS), and Chemin vers la mer (CVM)—along with the autonomous city of Nerfoy (NF). The 2014 constitutional amendments to the Constitution of Montesayette redefined the union as "one indissoluble federated Commonwealth" and made no provision for state secession, which was previously possible. All provinces are subdivided into departments and municipalities, except Hamicourt and Nerfoy, which are organized into arrondissements. Municipal divisions fall into three main categories: city, county, and canton. These are further subdivided into districts, towns, or villages.
Provinces have the general power to legislate, except in areas where the constitution grants exclusive powers to the federal government. The federal government can only legislate on matters specified in the constitution, but its laws take precedence over provincial laws in case of conflict. Since the Fourth Commonwealth, the federal government's power relative to the provinces has significantly increased due to broader interpretations of its enumerated powers and the provinces' heavy dependence on federal grants.
Each province has a unicameral legislature called the Legislative Council, except for Nerfoy, which has a City Assembly. The head of government in each province, directly elected, is known as the First Minister except in Hamicourt and Nerfoy, where the head of government is called the Governor. The federal government appoints a commissioner-general to represent its interests in each province. Beyond this representation, provinces have full autonomy: they can enact their own basic laws, organize their local governments as they see fit, and manage their natural and financial resources.
Foreign relations
Military
Law enforcement and crime
Human rights
Economy
Montesayette has a mixed-market economy with significant government involvement and economic diversity. As of 2023, it ranks as the world's 12th-largest by nominal GDP. The country’s labor force numbers around 33 million, with an unemployment rate of 3.5% as of April 2024. According to the Department of Employment and Workplace Relations, 13.6% of the population—about 8.8 million people—lives in poverty. As of July 2024, government debt is at 98.1% of GDP. Montesayette's currency, the Montesayettean pound, is issued by the Monetary Authority of Montesayette.
Montesayette's economy is highly diverse. The service sector makes up about two-thirds of both the workforce and GDP, while the industrial sector contributes around 20% to GDP and employment. The primary sector, including mining and agriculture, accounts for roughly 13% of GDP. Although Montesayette implements protectionist policies in certain industries, particularly agriculture, it has at times advocated for free trade in Northern Ecros through its membership in the Eastern Ecros Free Trade Area (EEFTA), aiming to boost its economic interests.
The Montesayettean government has historically played a key role in the economy. After the Third Commonwealth ended in 1972, policies like indicative planning and nationalization fueled two decades of unprecedented economic growth, known as the Vingt d'Or. Beginning in 1986, the Dufour administration reduced regulations and state involvement in the economy. By 2023, most major enterprises were privately owned, with state control limited to transportation, defense, telecommunications, broadcasting, and mining, which together account for 22% of GDP.
Agriculture, forestry and fishing
Science, technology and energy
Transportation
Demographics
| Rank | Provinces | Pop. | Rank | Provinces | Pop. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Nerfoy  Audrecelles City |
1 | Nerfoy | Nerfoy | 14,094,034 | 11 | Tsarollais | Grand Ouest | 1,527,772 |  Chenonceaux  Lavignole |
| 2 | Audrecelles City | Audrecelles | 7,721,208 | 12 | Montheries | Nouvelle-Darbonnay | 1,467,241 | ||
| 3 | Chenonceaux | Pays de la Sandrine | 5,347,221 | 13 | Bigòrra | Nouvelle-Darbonnay | 1,354,859 | ||
| 4 | Lavignole | Nouvelle-Darbonnay | 2,982,150 | 14 | Elna | Pays de la Sandrine | 1,299,811 | ||
| 5 | Hamicourt | Hamicourt | 1,961,347 | 15 | Poetàe | Nouvelle-Darbonnay | 1,027,643 | ||
| 6 | Brumeville | Sud-Val de Sandrine | 1,923,416 | 16 | Cerdagne | Grand Ouest | 896,584 | ||
| 7 | The Potences | Pays de la Sandrine | 1,857,923 | 17 | Présidie | Pays de la Sandrine | 842,690 | ||
| 8 | Frejús | Pays de la Sandrine | 1,721,785 | 18 | Milly-en-Gâtinais | Île-de-Fleurs | 712,815 | ||
| 9 | Montmarin | Sud-Val de Sandrine | 1,643,642 | 19 | Perpinhan | Pays de la Sandrine | 676,854 | ||
| 10 | Tolosa | Sud-Val de Sandrine | 1,589,266 | 20 | Lasseran | Pays de la Sandrine | 654,278 | ||
Religion
Languages
Education
Health
Culture
Art
Architecture
Literature and philosophy
Entertainment
Holidays
Montesayette has 16 nationally recognized public holidays. Since 1973, the country has adopted a long-weekend holiday system, moving public holidays that fall on weekends to either the preceding Friday or the following Monday. The public holidays in Montesayette are as follows: New Year's Day on January 1, Good Friday, Easter Monday, Eid al-Fitr, the three-day Lunar New Year, Unification Day on March 24, Labour Day on May 1, Commonwealth Day on May 13, Ascension Day, Whit Monday, Armistice Day on August 26, Eid al-Adha, All Saints' Day on November 1, Children's Day on November 20, Christmas Day on December 25, and St. Stephen's Day on December 26.