Difference between revisions of "Savotta (Romanyan province)"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[ | + | {{Infobox former subdivision |
| + | |native_name = {{aut|Savotta Provincia}} | ||
| + | |conventional_long_name = | ||
| + | |common_name = Savotta | ||
| + | |subdivision = [[Roman province|Province]] | ||
| + | |nation = the [[Romanyan Empire]] | ||
| + | |era = [[ancient history|Antiquity]] | ||
| + | |capital = [[Savotta (city)|Savotta]] | ||
| + | |p1 = | ||
| + | |s1 = Savottan Empire | ||
| + | |title_leader = | ||
| + | |image_map = Province of Savotta.png | ||
| + | |image_map_caption = Territory administrated by the Province of Savotta, circa 100 BC. | ||
| + | |life_span = | ||
| + | |year_start = 160 BC | ||
| + | |event_start = | ||
| + | |year_end = 546 AD | ||
| + | |event_end = | ||
| + | |today = [[Salisford]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | '''Savotta''' was an ancient [[Romanyan Empire|Romanyan province]] located in the northwest of Sur, roughly corresponding to the modern northern territories of [[Salisford]], including its northern coastline, parts of the Salisfordian central highlands, and western plain | + | '''Savotta''' was an ancient [[Romanyan Empire|Romanyan province]] located in the northwest of Sur, roughly corresponding to the modern northern territories of [[Salisford]], including its northern coastline, parts of the Salisfordian central highlands, and western plain. |
| − | + | == Historical background == | |
| − | + | === Pre-Italic Savotta === | |
| − | == | + | === Settlement by Italics === |
| − | == | + | === Classical Egittan Civilization === |
| + | {{main|Classical Egitta}} | ||
| − | == | + | === Unification of the Egittan Republic === |
| + | {{main|Egittan Republic}} | ||
| − | ==Notable Savottans== | + | === First Egittan War === |
| − | *[[Servilius Geminus]], legate, one of the Romanyan commanders at the [[Battle of the | + | |
| + | === Conquest in the Second Egittan War === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Romanyan province === | ||
| + | {{main|Romanyanization of Savotta|Egitto-Romanyans}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Capital of the South === | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Military presence == | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Notable Savottans == | ||
| + | *[[Servilius Geminus]], legate, one of the Romanyan commanders at the [[Battle of the Xichútepa River]]. | ||
| + | *[[Quintus Nonus]], general, major [[New Kingdom of Illyricum|Illyrian]] leader during the [[Illyrian reconstitution]]. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Legio XVII]] | *[[Legio XVII]] | ||
| + | *[[Savottan Empire]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 23:21, 5 April 2024
| Savotta Provincia | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Province of the Romanyan Empire | |||||||
160 BC–546 AD | |||||||
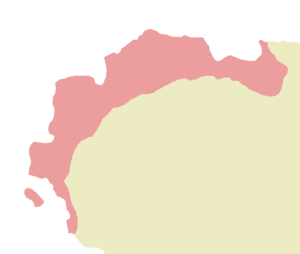 Territory administrated by the Province of Savotta, circa 100 BC. | |||||||
| Capital | Savotta | ||||||
| History | |||||||
| Historical era | Antiquity | ||||||
• Established | 160 BC | ||||||
• Disestablished | 546 AD | ||||||
| |||||||
| Today part of | Salisford | ||||||
Savotta was an ancient Romanyan province located in the northwest of Sur, roughly corresponding to the modern northern territories of Salisford, including its northern coastline, parts of the Salisfordian central highlands, and western plain.
Historical background
Pre-Italic Savotta
Settlement by Italics
Classical Egittan Civilization
Unification of the Egittan Republic
First Egittan War
Conquest in the Second Egittan War
Romanyan province
Capital of the South
Military presence
Notable Savottans
- Servilius Geminus, legate, one of the Romanyan commanders at the Battle of the Xichútepa River.
- Quintus Nonus, general, major Illyrian leader during the Illyrian reconstitution.