Difference between revisions of "Romanyan Empire"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
| coa_size = 100 px | | coa_size = 100 px | ||
| symbol_type = Imperial [[Aquila (Romanyan)|aquila]] | | symbol_type = Imperial [[Aquila (Romanyan)|aquila]] | ||
| − | |symbol_type = | + | |symbol_type = Imperial [[Aquila (Romanyan)|aquila]] |
|symbol_type_article = <!-- Link target under symbol image. Default: Coat of arms of {{{common_name}}} --> | |symbol_type_article = <!-- Link target under symbol image. Default: Coat of arms of {{{common_name}}} --> | ||
|image_map = RomanyanEmpireMap2.png | |image_map = RomanyanEmpireMap2.png | ||
Revision as of 14:40, 9 April 2022
Romanyan Empire Imperium Romanum | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35 BC–AD 680 (unified) AD 680–1350 (Savottan Empire) | |||||||||
Imperial aquila
| |||||||||
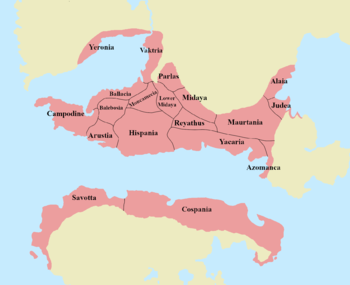 | |||||||||
| Capital | Romanya | ||||||||
| Common languages | Ayreoshubic, Romanyan Iberic | ||||||||
| Religion | Romanyan Paganism, Romanyan Christianity | ||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Romanyan | ||||||||
| Government | Semi-elective, functionally absolute monarchy. | ||||||||
| Historical era | Ancient | ||||||||
• Empire Established | 35 BC | ||||||||
• Fall of Romanya | 680 AD | ||||||||
| 1350 AD | |||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• 25 BC | 56,800,000 | ||||||||
| Currency | Sestertius, Denarius, Aureus, Solidus | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of |
| ||||||||
The Romanyan Empire (Romanyan Iberic: Imperium Romanum) was one of the largest nations in Terraconservan history based mostly in southern Ecros and northern Sur. The empire controlled most of the coastline of the Alzanub Sea and controlled territories on all three continents: Ecros, Ostlandet, and Sur. The empire was one of the most influential in history as its cultures and languages have been adopted by multiple nations.

