Assoria
Assoria | |
|---|---|
|
Symbol of Ashur, the ancient Assorian national deity | |
| Capital | Ashur |
| Official languages | |
| Common languages | Akadian Aramaic |
| Demonym(s) | Assorian, Ashurian |
| Government | Monarchy |
| King | |
| Historical era | Bronze Age |
• Established | 2500 BC |
• Disestablished | 600 BC |
| The Ancient Caelean Coast |
|---|
 |
| Regions and states |
| Archaeological periods |
| Languages |
| Literature |
| Mythology |
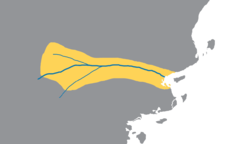
Assoria, also known as Ashuria, was an Alaian kingdom and empire on the Ancient Caelean Coast, which existed as early as the 25th century BCE (in the form of the city-state of Ashur) until its collapse in 600 BCE. This vast period is divided into the Early Period (2500-1900 BCE), Old Assorian Kingdom (1900-1580 BCE), Middle Assorian Empire (1580-900 BCE) and Neo-Assorian Empire (900-600 BCE). From 600 BCE following the fall of the Neo-Assorian Empire until the 14th century AD, Assoria survived as a geopolitical entity dominated by foreign powers, including Babylonia and the Romanyan Empire.
Assoria was a Semitic-speaking nation. From the Early Period until beginning of the Middle Assorian Empire, the common language was the Assorian dialect of Akadian. Aramaic rose to prominence during the Neo-Assorian Empire.
The descendants of the Aramaic speaking people of the Neo-Assorian Empire formed the Kingdom of Aramea in 1300 CE. until they were conquered by the Empire of Terranihil in 1600 CE. A significant population of Assorian or Aramean people is present in modern day eastern Terranihil.
Contents
Name
The name "Assoria" is derived from the original capital of the Assorian state, the ancient city of Ashur, which dates back to c. 2500 BC. It is originally one of several Akadian-speaking city-states.
Pre-history
In prehistoric times, the region that was to become known as Assoria was home to Neanderthal cultures. The Akadian-speaking people who would eventually found Assoria entered Alaia at some point during the late 4th millennium BCE (c. 3500–3000 BC), intermingling with the earlier Sumerian-speakers, who came from the north.
The city of Ashur, among others, existed since before c. 2500 BCE, although it was ruled by other Sumerian city-states. According to the Biblical generations of Noah, in Genesis chapter 10, the city of Ashur was founded by Ashur the son of Shem. However, the much older attested Assorian tradition itself lists the first king of Assoria as the 25th century BCE Tudia. It is highly likely that the city was named in honour of its patron Assorian god with the same name.
History
Early Period (2500–1900 BCE)
The city of Ashur, with several other Assorian cities, were established by 2500 BC. They were likely initially Sumerian-dominated administrative centres. Little is known about the early history of the city-state of Assoria. The earliest Assorian king recorded was Tudia.
Akadia and Neo-Sumerian Empires (2300–2100 BCE)
During the Akadian Empire (2300–2100 BCE), the Assorians, like all Semitic Alaians as well as Sumerians, became subject to the dynasty of the city-state of Akad. The Sumerians were eventually absorbed into the Akadian (Assorian-Babillonian) population.
Assorian rulers were subject to Sargon the Great and his successors, and the city of Ashur became a regional administrative center of the Empire. Assorian traders spread the use of writing in the form of the Alaian cuneiform script to Malgax and the Zahjeddah. However, towards the end of the reign of Sargon, Assoria rebelled against him.
Ayreoshubic Empire (2100-1900 BCE)
The Akadian Empire was conquered by the Ayreoshubic Empire in 2100 BCE, so Assoria was under Ayreoshubic rule.
Old Assorian Kingdom (1900–1580 BCE)
Ushpia was the first fully independent king of Assoria and is traditionally held to have dedicated temples to the god Ashur in the city of the same name.
In c. 1850 BCE, a king named Pumarashur I came to the throne of Assoria, who is debated as to whether he was the founder of a new dynasty or a descendant of Ushpia. He conducted building projects in Ashur. Assoria began to expand trading colonies into the north. He aso appears to have conducted military campaigns in southern Alaia, either in conquest of city-states or in order to protect his fellow Akadian-speakers from incursions by Elamites and/or Amorites.
He was succeeded by the long reigning Erishum I (1825–1785 BCE) who is notable for one of the earliest examples of written legal codes. These policies were continued by the following kings.
King Shamshiadad I (1670–1650 BC), although he claimed Assorian ancestry, is regarded as a foreign Amorite usurper by later Assorian tradition. However, he greatly expanded the Old Kingdom, incorporating the northern half of Alaia and much of the coast into his empire.
After Ishmedagan I's death Assoria was reduced to vassalage by Hammurabi. The folowing three Assorian kings were subservient to Hammurabi, who also took ownership of Assorian trading colonies, thus bringing an end to the Old Assorian Kingdom in 1630 BCE.
Middle Assorian Empire (1580-900 BCE)
However, Babylonian rule proved short lived, with it rapidly collapsing after the death of Hammurabi c. 1590 BCE. An Assorian governor named Puzursin deposed a foreign Amorite puppet of the new Babylonian king. A king called Adasi (1550–1530 BCE) finally restored strength and stability to Assoria, ending the civil unrest that had followed the ejection of the Babylonians and Amorites.
There followed a long, prosperous and peaceful period in Assorian history from about 1500 to 1350 BCE. Mutiple rulers had peaceful and relatively uneventful reigns. Assoria entered a period of decline and civil unrest in which it lost much of its peripheral holldings. However, the command of several strong king led to the retaking of these territorie by 1100 BCE. The Empire continued to gradually expand. In 1000 BCE, Assoria and Babylonia engaged in wars for about a century until Assoria conquered its rival in 900 BCE.